What is Data Lifecycle Management
17 min read
What is Data Lifecycle Management
With the rise of multinational corporations came new problems, unforeseen by the businesses of the “old world”. One such problem is the problem of data lifecycle management. And yet, despite being crucial to enterprise users, the term remains relatively vague. So let’s reintroduce and define the most important notions related to data lifecycle management.
Before we delve deeper, it’s essential to distinguish between data and information, which are often used interchangeably, but in the business environment, their difference is vast. In essence, we can differentiate data from information in the same way we differentiate fact from meaning. Following that, data is a collection of raw, decontextualized, and unorganized facts that carry no significance or purpose on their own. On an even deeper level, we can talk about data points, which are individual and often unrelated units of data. On the other hand, information is that same data organized and placed into a specific context. Fundamentally, information is the result of diligent analysis and interpretation of data. Where data is just a collection of figures, numbers, and graphs, information represents how data is utilized.
Let’s take the volatility of fuel prices as an example. If we take the fact that fuel prices are rising, we can see it is pure data and doesn’t say much on its own accord. But if we add context to it, it could mean that rising fuel prices will mean that company’s cost of transport and production will rise, forcing them to increase the final price of their product, which will ultimately burden the end consumer. Now we’re talking about information.
Considering this, it becomes apparent that, in this context, we can talk about two types of lifecycle management: Information Lifecycle Management and Data Lifecycle Management. Fundamentally, Information Lifecycle Management is a practice-driven approach that aligns the totality of a company’s information with the proper tools to manage its lifecycle. Therefore, Information Lifecycle Management (ILM) can be defined as a policy that entails consistent information management, and a collection of strategies companies implement to manage information from its production to its disposition. On the other hand, Data Lifecycle Management (DLM) is a policy-based approach that concerns itself with how to best manage the flow of data throughout its lifecycle – from creation to its final deletion, with the ultimate goal of achieving and preserving data integrity.
In the end, it can be said that information lifecycle management practices concern themselves with how important, relevant, and accurate any given information or data is. On the other hand, data lifecycle management tries to automate and define all the stages of the data lifecycle: how to create the correct data, how to utilize it, and finally, how and when to delete it. We will now set the information lifecycle management aside and focus on the data lifecycle management, which, accidentally, of course, falls under our area of expertise.
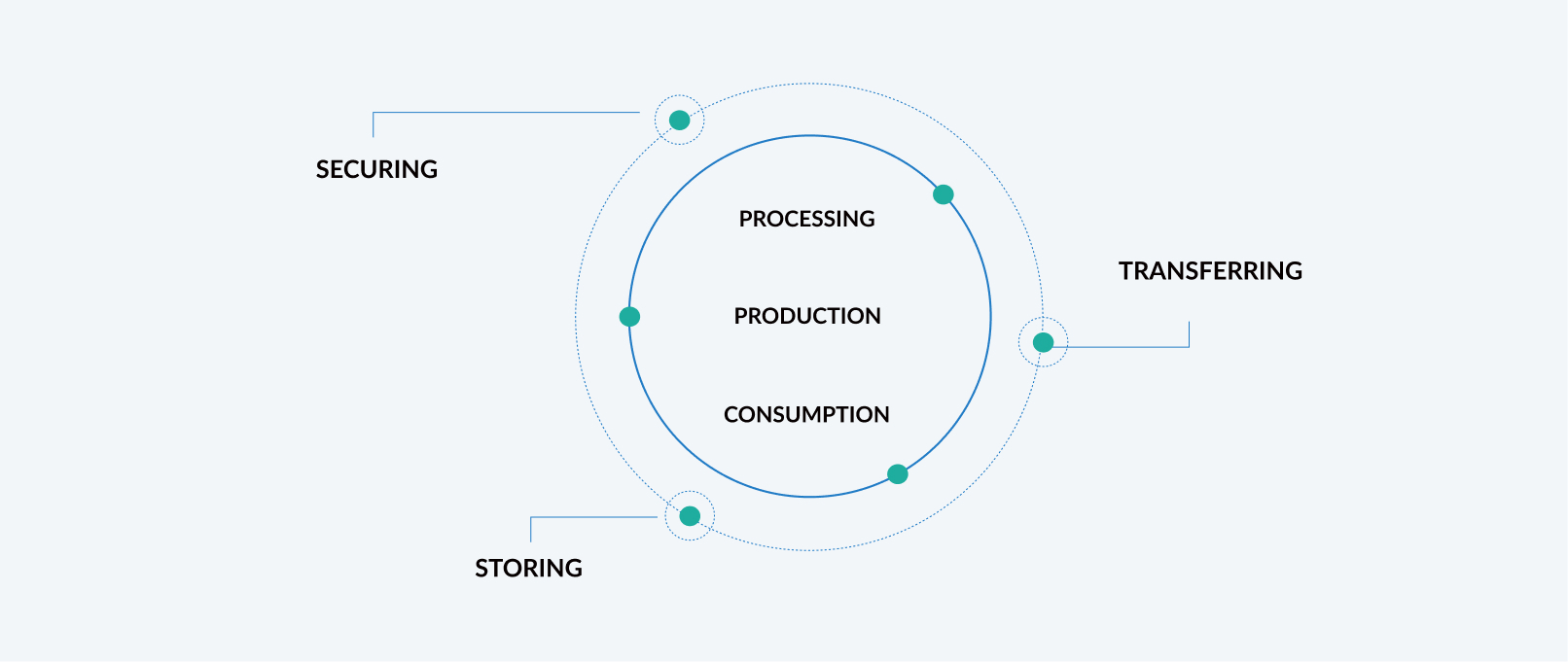
InnoBoost – Who are we and what we do
InnoBoost is a team of innovators, experts, and data scientists specialized in implementing cutting-edge technologies to manage the lifecycle of your data. Our expertise extends over all six stages of data lifecycle management: production, processing, consumption, transfer, storing, and securing. Through the years, we’ve developed a complex network of partners and collaborators who help us in our endeavor by providing a technological foundation for tailoring and adapting our solutions to your needs.
To be able to implement the best data management solutions for your business operation, our experts and scientists have mastered the areas of Artificial Intelligence, Internet of Things (IoT), Quantum Computing, Intelligent Edge, Cloud Technology, Software-Defined networking, Orchestration technology, Quantum Key Distribution (QKD), and so much more. If you’re still in doubt or you’re not sure how these advanced technologies can help your business, here’s a short list of how having an optimized data lifecycle benefits you:
- Compliance with data regulations
- Quick access to the right data
- Improved operational efficiency & agility
- Improved customer experience
- Improved data security
- More effective data governance
- Overall cost reduction
Below you can find detailed descriptions of how we use and implement our solutions to all six stages of data lifecycle, but if you want to take the quick road, don’t hesitate to reach out and have a chat with our experts here.
What is Data Creation?
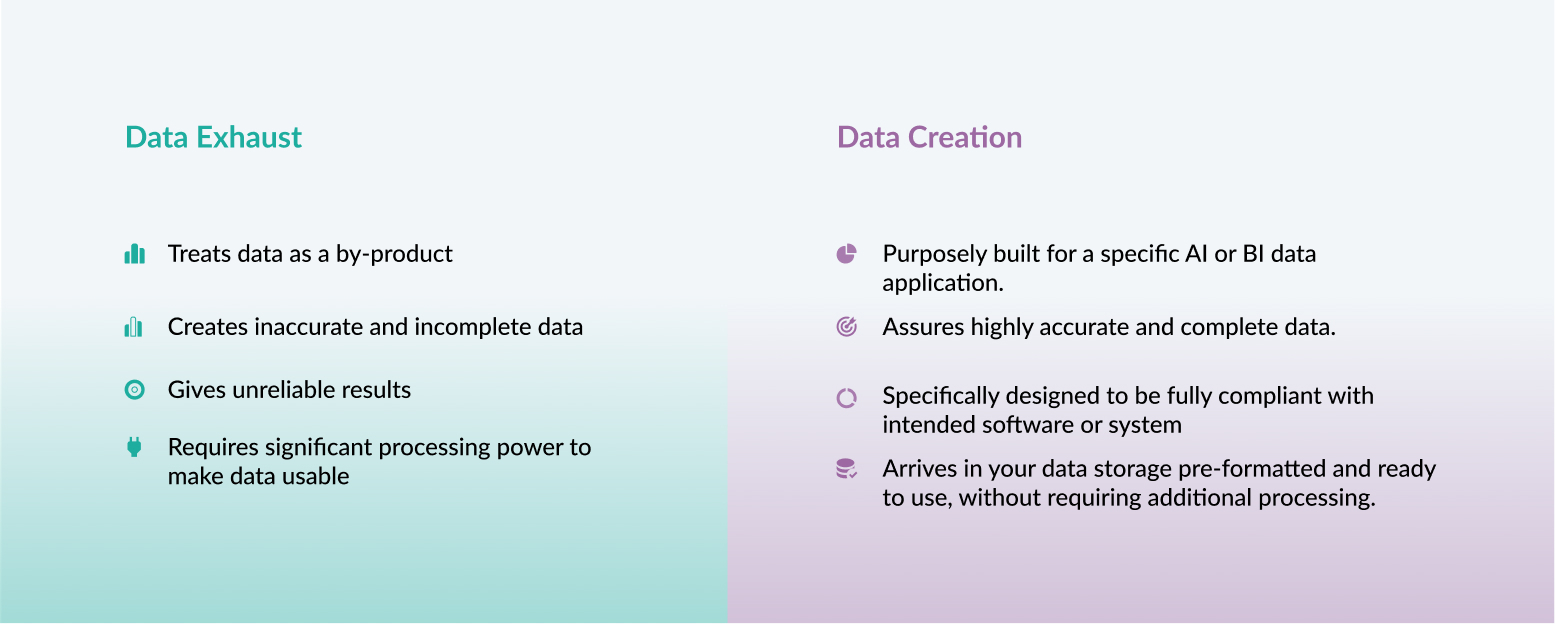
When it comes to data lifecycle management, one of the biggest mistakes companies make is using data exhaust instead of a data creation strategy. For those who don’t know, data creation can be described as a process of creating data exclusively for artificial intelligence and other advanced data processing applications. On the other hand, data exhaust is a process that treats data as a by-product of the pre-existing systems, adopting it for purposes it was not initially intended.
Dealing with data exhaust is tedious, time-consuming, and filled with technical challenges. It often produces unreliable results that require significant processing to become usable by the data research team. Adopting the data creation strategy, your company creates accurate, complete, and purposefully built data for sophisticated systems and software, requiring no additional processing and optimizing before it can be stored or used. To help you create a system that produces relevant, high-quality data that consistently brings value to your company, we have developed expertise and mastery in implementing cutting-edge technologies, such as the Internet of Things (IoT) and the Intelligent Edge. Here’s a short introduction to what the IoT and the Intelligent Edge are and how they can be utilized.
Internet of Things
The Internet of Things (IoT) is a term that describes the interconnectedness of different physical objects (the Things) that are imbued with sensors, software, and other technologies that allow them to exchange data with other systems or devices via the internet. These “Things” can range from the most mundane everyday objects, like security cameras, household appliances, and smart devices, to the most advanced industrial and embedded systems, machine learning, and so on. When “Things” communicate, data is collected from these devices and is transferred to the central location, from where it is processed and consumed, ultimately contributing to intelligent application control, minimization of human effort, task automation, safety, and easier real-time information access.
Intelligent Edge
With the Intelligent Edge, technology developed in cooperation with our partners at IBM, we can provide you with advanced solutions that allow you to analyze data at the same site where that data is generated. That means that, instead of sending data out to the central data center or another third party, the data processing happens at the location where the data is generated. The result is an all-around solution that drastically improves the quality of the data your systems create, all while reducing latency, overall costs, and security risks. Combined with the IoT, Intelligent Edge provides you with a solution that ties all your devices into a singular network with superb efficiency, while being able to process all those terabytes of data at the place where it’s created.
What is Data Processing?
Even the most advanced data creation systems are futile if the systems in place cannot make sense of the created datasets. In such scenarios, businesses are forced to work with an existing database that has poor description and stored information. They consequentially risk security breaches, violation of laws and regulations, running out of storage capacity, or simply saturating your processing systems with duplicated, inconsistent, and rogue data. Processing complex data slowly becomes impossible as one thing adds up to another. With the help of advanced technologies such as quantum computing, AI, and High-Performance Analytics, we can guarantee that your business gets the best and most advanced data processing systems & protocols currently available, improving the overall efficiency and profitability of your business processes.
But first, to precisely explain how our data processing solutions can help your business, it’s helpful to define what data processing is. A straightforward definition would be that data processing is collecting and manipulating digital data to produce sets of meaningful information. The larger the company, the larger the volume and complexity of the data that needs to be processed.
High-Performance Analytics technology
High-Performance Analytics technology offers a comprehensive and integrated workload management solution that, aside from redefining how your company aggregates computing power to deliver more advanced analytical performance, can provide a heterogenous and scalable architecture that acts as a strong support to your existing high-performance computing. Successfully implemented High-Performance Analytics significantly increases worker productivity and hardware usage while reducing system management costs.
Artificial Intelligence
When it comes to processing big data, implementing High-Performance Analytics technology usually comes hand-in-hand with AI-driven data processing. Our Artificial Intelligence solutions allow you to process large-scale heterogeneous data with the help of advanced pattern recognition, machine learning, and deep learning, as well as processing more “traditional” modes of data such as data generated from the Internet of Things, sensing networks, communication, and more.
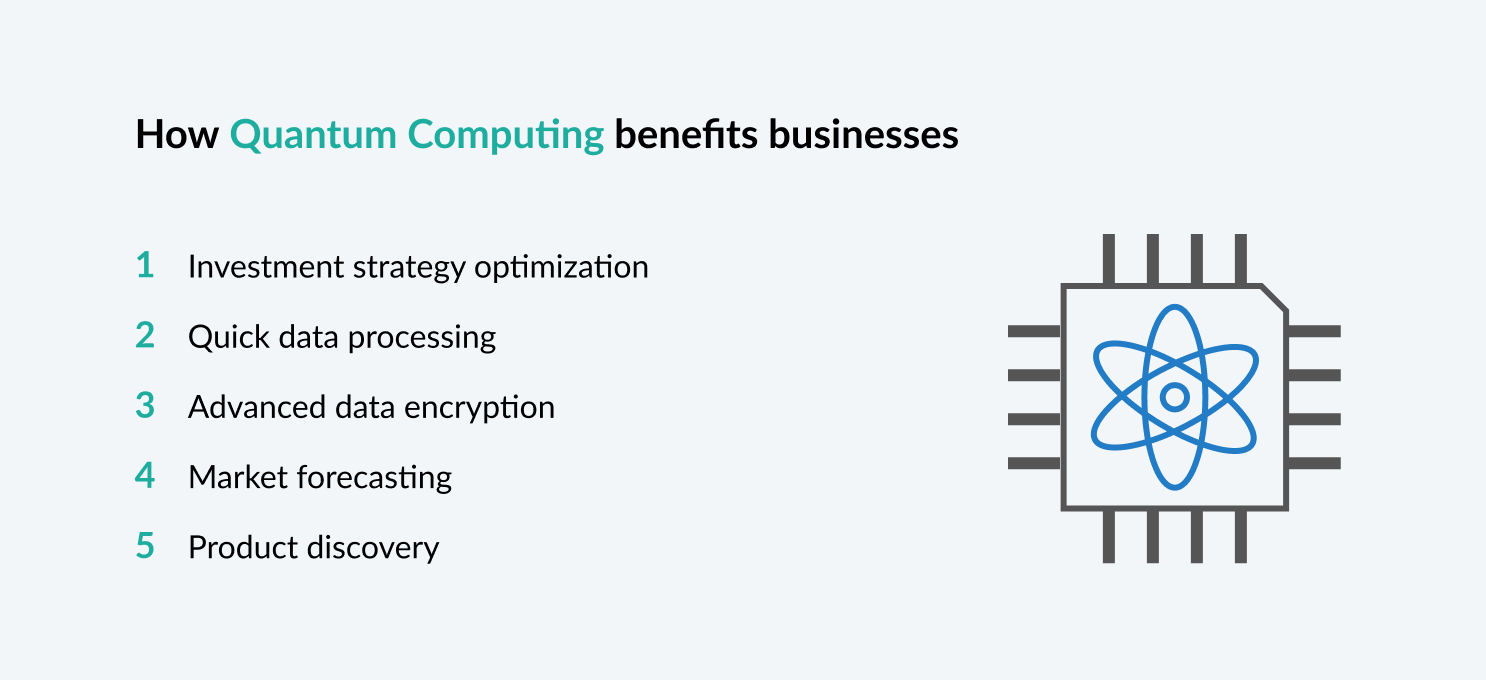
Quantum Computing
And lastly, in order to provide the most precise and fastest data processing power currently available, there’s InnoBoost quantum computing technology. Quantum computing-driven data processing will allow your business not only to process data at lightning speed but will allow you better investment strategy optimization, advanced data encryption, product discovery, and market forecasting, and help you solve other intractable problems.
What is Data Consumption?
In this age where everything is becoming online, virtual, and remote, the problem of data consumption is becoming increasingly severe. The traditional way of accessing data, where it used to be stored in the organization’s headquarters or on the cloud and accessed via point-solution or standardized procedures, is no longer viable. While each business, compartment, or an individual access and works with the same set of data, how they consume that same data can be radically different. That’s why more and more enterprises are adopting a holistic approach to data consumption to account for ever-changing ways of how data is accessed and consumed.
One could ask what a holistic approach to data consumption means, so here’s a short answer. In today’s world, when it comes to how they want their data to be consumed, businesses usually have three solutions to choose from private cloud, public cloud, or hybrid cloud. However, it is not unusual for companies not to be able to adapt their operations to one of these options entirely but require an agile cloud environment tailored to their needs. We call this fourth option the multi-cloud solution. And with the help of IBM and RedHat OpenShift technologies, we can construe custom and tailored solutions to fit all your needs. To help you understand how InnoBoost can help your data consumption, here’s a short introduction to each of these different cloud technologies and how businesses like yours find a use for them.
Private Cloud
Private cloud environments are usually employed for in-house usage, meaning that companies (or third-party providers) develop in-house cloud servers for their private use. Since they’re hosted on private servers, a private cloud environment offers more control over security. Their start-up costs are usually high, but maintenance fees remain relatively low. Moreover, their high flexibility allows businesses to develop personalized functionality and scalability, as the storage can be added or removed according to your needs.
Public Cloud
Public Clouds as the name suggests, are publicly available cloud servers. You probably already know about some public cloud providers: Google Cloud Platform, Microsoft Azure, IBM Cloud, and others. They offer low start-up costs and fees over time and require little to no maintenance. And since the storage can be expanded without limit, scalability is one of the most decisive advantages of the public cloud. However, their weak side is their lack of flexibility, inability to meet the business’s specific needs, and security, as clients depend on the provider to secure their data. And last, between the private and public cloud environments is the hybrid cloud, the combination of the two.
Hybrid Cloud
Hybrid cloud uses the resources from both the private and the public cloud to create a more varied environment, allowing you to reap both benefits. This cloud model will enable you to store vulnerable and secret data in the private cloud, and less private data can be accessed from the public cloud. A hybrid cloud environment has higher start-up and maintenance costs (but are still lower than exclusively using a private cloud). It also allows you to migrate easily to the type of cloud you need.
Multi-cloud
Although it might sound similar to the hybrid cloud, multi-cloud implies using several different public and private clouds to host your data, as opposed to mixing singular private and public clouds. A multi-cloud environment is the most cost-effective solution that fulfills all your cloud needs. It also allows you full autonomy and independence from using just one cloud provider. And since you can branch out to different providers whenever the need emerges, you gain almost infinite scalability. By putting all these different cloud options at your disposal, our expertise and experience can deliver the right solution to all your problems with data consumption.
What is Data Transfer?
How your company transfers files and data can make or break your business. Poorly managed data transference brings an array of risks with it. From security concerns to slow and unreliable communication between partners, compartments, and individuals, every aspect of your enterprise suffers if data transferring is not fast and seamless.
There are three most significant challenges companies have concerning data transferring. Since data transference often implies moving data beyond the scope of your company, data security is of utmost importance. Next is the data complexity. As data transference involves thousands of files and data points, robust reporting and tracking software is a must. And the third one is performance, as data transfer often deals with huge files that require a lot of time for uploading, processing, and downloading. The old way of tackling these challenges involved using dedicated devices for controlling network traffic, like routers and switches. New ways involve somewhat more sophisticated methods, like Software-Defined networking.
Software-Defined Networking (SDN)
As technology opens up new horizons, it allows us to help companies like yours build the best data-transferring protocols possible. Consequentially, we have developed strong expertise in Software-Defined Networking (SDN). SDN is an approach to data transferring that relies on network-based application programming interfaces (APIs) to establish communication with its underlying infrastructure and regulate and direct traffic on any given network.
Adopting SDN is a significant improvement from the traditional way of networking, as it allows you to:
-
- Increase control with superb flexibility and speed
- Customize network infrastructure
- Build robust network security
The crucial difference between Software-Defined Networking and traditional networking is how their infrastructure is set up. As the name says, SDN is software-based, while traditional networking relies on hardware to fulfill its purpose. This allows SDN to have superior flexibility, enabling administrators to have greater control over the network, change the configuration as they see best, provide additional resources, and optimize network capacity to fit your company’s needs.
What is Data Storage?
Having reliable data storage is the cornerstone of your business. In cooperation with our partners at IBM, we have developed the most secure, innovative, and enduring methods for storing your data.
Data storage fundamentally implies storing, recording, and saving digital data for future use. Over the decades, technological progress has given birth to many data-storing technologies, some more volatile than others. Physical hard drives, disks, USB drives, virtual cloud storage, or magnetic tape are just some of the many data storage systems available to users and companies. Depending on the size and volume of your business, you might require some or all of them to operate successfully.
However, despite all the available options, modern organizations that rely on high-level computation require data storage that can contain the enormous volume of data that their projects and systems like AI, machine learning, and IoT produce. Companies are risking game-ending catastrophes without a strong backbone in data storage to protect them from disaster, fraud, or system failure.
Considering the best data storage solution, every leader should ask the most critical question: how much money can an efficient data storage system save for your business, and what can it do to protect your company’s data and information? To give a proper answer, it’s essential to consider how data storage that is fully adapted to your needs can benefit your whole organization:
-
- Data preservation
- Data accessibility
- Data continuity
- Data recovery
- Data security
- Storage capacity
Having all those benefits in mind, here are the cutting-edge data-storing technologies that we at InnoBoost have developed expertise for:
Cloud Storage
Cloud Storage is the data computing model that allows individuals and organizations to store data online through a cloud provider, either via the internet or on a dedicated private network connection. Cloud provider ensures that the data is stored securely and that servers and infrastructure are maintained regularly. Providers also must guarantee that your data is accessible whenever you need it and that you never run out of storage capacity. The main benefit of having high-quality cloud data storage is that it removes the need to have your own storage infrastructure, making your data storing system agile, scalable, and durable.
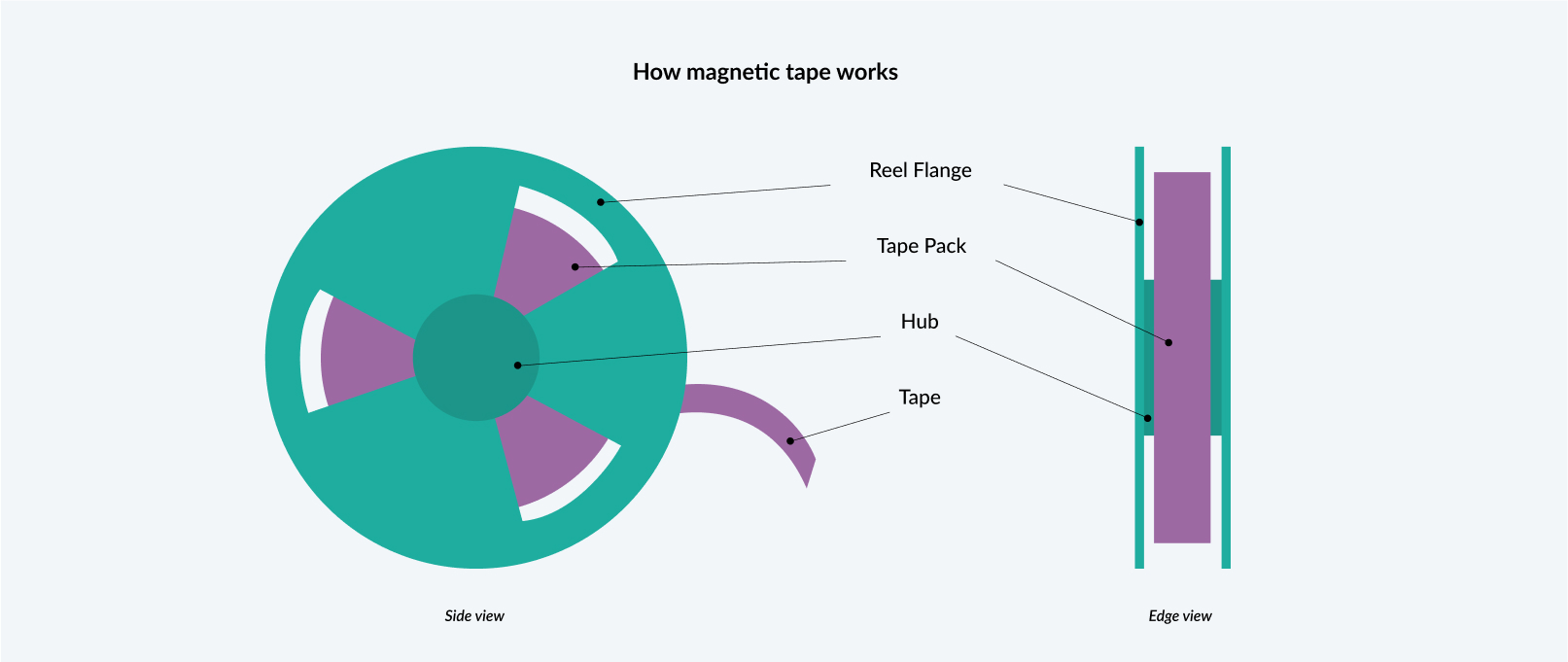
Magnetic tape
Despite being around for over 60 years today, the reliability, security, and cost-effectiveness of magnetic tape are still unmatched. Many businesses rely on magnetic tape as their primary backup system. The main benefits of having magnetic tape as your data storage system are its capacity, immunity to cyberattacks, low cost, broad device compatibility, energy efficiency, and low volatility.
Distributed File System (DFS)
Distributed File Systems is data storage system that relies on distributing files on multiple servers or locations. It allows applications to access or save individual files as they would do with the local ones, making them accessible from any network or station. The primary purpose of the DFS is to allow users to share their resources through a Common File System (CFS), which connects many individual workstations and mainframes through the Local Area Network (LAN). The main benefits of the DFS are: it allows multiple users to store data in the same location, it makes remote data sharing possible, it improves data availability, access speed, network efficiency, and data transparency (even in the case of server failure).
What is Data Security?
The importance of data security cannot be overvalued. A robust security system that protects your data against corruption, cyberattacks, unauthorized access, and other unwanted actions saves your company from financial loss, trust degradation, reputation harm, and brand erosion.
Data security is a systematic way of keeping digitally stored information safe. It’s a process that touches upon every stage of the data lifecycle, from data creation to data consumption. It does not only include providing online or physical data security, but application security, organizational policies, protocols, and procedures.
Ideally, data security entails using different sets of tools and technologies that improve your company’s visibility into where its most important data is stored and how it is used. If implemented properly, strong data security guards your assets against cybercrime, insider and outsider threats, and human error (one of the leading causes of data breaches). Modern industry standards require every data security system to ensure that they cover the following:
-
- Encryption
- Data masking
- Sensitive file redaction
- Automatic reporting
- Regulation adherence system
To ensure your data has the best security today’s technological advancement can offer, we have several solutions at your disposal:
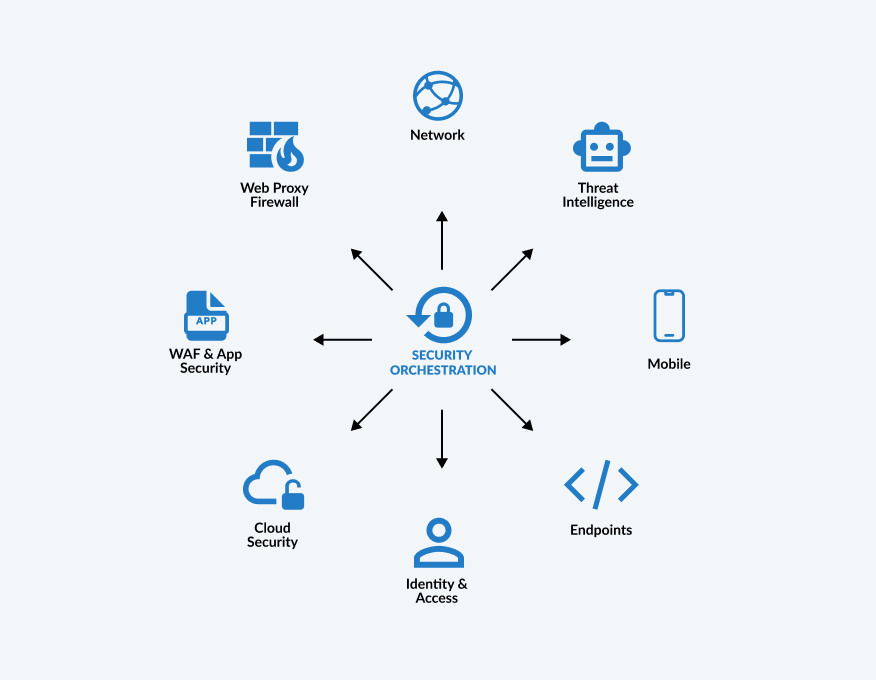
Security orchestration Technologies
Security Orchestration is an advanced technology that allows multiple security solutions to be combined into a streamlined system that uses the best of their protection and security capabilities without hindering one another. Using orchestration technology as your dominant data security system allows for a quick data breach response, increased efficiency, and streamlined IT processes.
Blockchain security
One of the most efficient security methods today, blockchain technology creates a virtual structure of data with unbreachable security qualities. At its foundation lie core tenets of cryptography, decentralization, and participant consensus, ensuring the fundamental trust in transactions protected by blockchain. Blockchain structures data into blocks, where each block contains information about a single transaction or bundle of transactions. Each new block connects to other blocks, making the whole structure a fortress that keeps your data safe and secured.
Quantum Key Distribution (QKD)
Quantum Key Distribution (QKD) is a technology that implements cryptographic protocols based on quantum mechanics, allowing two workstations to produce a random secret key visible only to them and which can be further used to secure or access stored data. This data-securing method uses quantum superposition, quantum entanglement, and quantum states to produce a key that is guaranteed to be secure. The most important (and unmatched) property of the Quantum Key Distribution is the possibility to let the two involved users know if a third party attempts to gain access to their data.
Homomorphic Encryption Technology
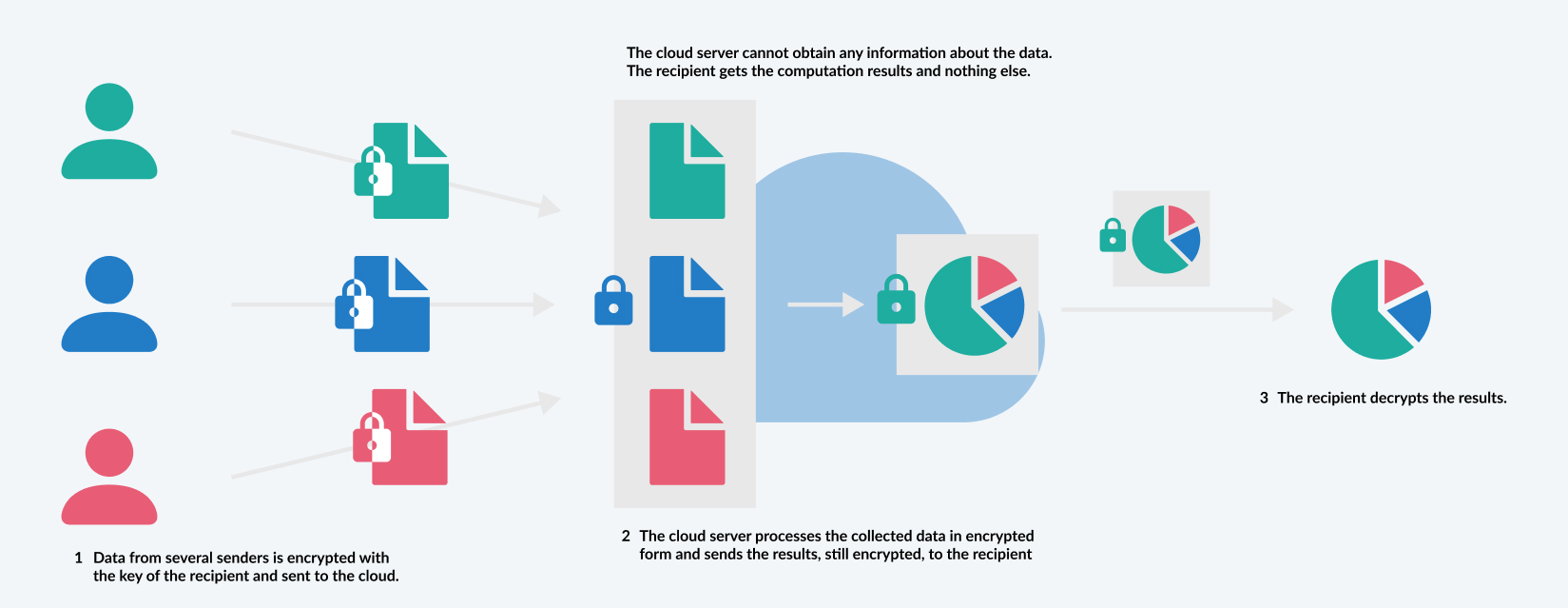
Homomorphic Encryption Technology relies on permitting users to process encrypted data without previous decryption or without needing a key, resulting in computations that are left in their encrypted form, which, once decrypted, create the same outputs as the ones which would be produced if the same operation had been performed on the unencrypted data. Homomorphic encryption technology is best used for privacy-preserved, outsourced storage, allowing data to be transferred and processed in a cloud environment while remaining encrypted.
You may also like…
Unlocking the Power of Custom AI with InstructLab
5 min readSummary In the dynamic landscape of artificial intelligence, the ability to create models tailored to unique business needs is more than a competitive edge—it's a necessity. InstructLab, a collaborative initiative from IBM and Red Hat, is revolutionizing AI...
Strengthening Authentication in the Digital Age with IBM Verify
5 min readSummary In today’s interconnected world, the importance of robust authentication systems cannot be overstated. As digitalization accelerates, safeguarding sensitive data and critical systems has become a top priority for businesses. Effective access...
From Data Chaos to Data Confidence: Real-World Use Cases of IBM Data Product Hub
5 min readSummary In a world where data streams in from every direction—transactions, patient records, supply chain logs, and more—businesses often face “data chaos.” Instead of powering innovation, their data sits scattered in different formats and systems, making it...